|
The Root Locus Method
The settling time t_{s} (0.2% criterion):
t_{s} = 0.5s ~ \rightarrow ~ t_{s} = \frac{4}{\sigma} ~ \rightarrow ~ \sigma = \frac{4}{0.5} ~ \rightarrow ~ \sigma = 8
This information can be obtained from the Root Locus Plot:
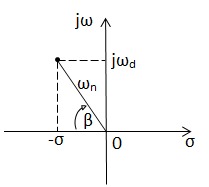 s = - \sigma \pm j \omega_{d}
\omega_{d} = \omega_{n} \sqrt{1-\zeta^2}
\sigma = \zeta ~ \omega_{n}
cos \beta = \zeta
s = - \sigma \pm j \omega_{d}
\omega_{d} = \omega_{n} \sqrt{1-\zeta^2}
\sigma = \zeta ~ \omega_{n}
cos \beta = \zeta
From the Root Locus Plot, a point of σ = -0,8 is found. If there is a point whose real part is -8 (zoom the plot near the region of interest to find a more accurate location for the point) and keeping in mind that all the points of a Root Locus Plot obey the relation:
1 + K. G(s)C(s) = 0
The gain, K, can be computed. Other information can be computed as well.
|

